Gynae Oncology Malaysia – Ovarian Cancer
-
24 May, 2021
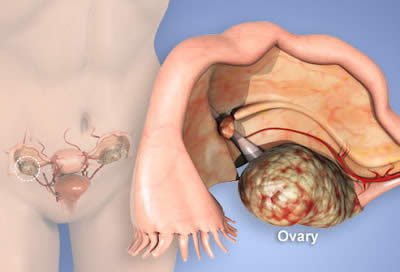
Ovarian cancer is recognized as the fourth leading cancer in Malaysia. Awareness of ovarian cancer risk factors among Malaysian women is low. There is a need for improved public understanding about ovarian cancer risks and provision of important information for health professionals about initiatives needed for future awareness, prevention and screening programs.
What Is Ovarian Cancer?
Current research suggests this cancer begins in the fallopian tubes and moves to the ovaries, the twin organs that produce a woman's eggs, and the main source of the female hormones estrogen and progesterone. Treatments for ovarian cancer have become more effective in recent years, with the best results seen when the disease is found early.
Ovarian cancer is typically portrayed as a "silent" killer, without much signs or symptoms until it is an advanced disease. The sooner the cancer is detected and treated, the better a woman's chance for recovery. Approximately 70% of women are diagnosed at late stage 3 or 4 of the disease.
What are the Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer?
These are the common symptoms associated with ovarian cancer:
- Increase in abdomen size
- Bloating
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Pain in the pelvic region
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained loss of weight (losing weight when you are not trying to)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Some may experience abdominal pain if a tumour is twisted, ruptured or bleeding
- Rarely, some experience irregular menstrual bleeding before or after menopause or excessive hair growth in young or elderly women
Where Does Ovarian Cancer Spread To First?
The most common areas it spreads to include the abdominal cavity and bladder. In later stages or with more aggressive cancers, it can spread to the liver and lungs as well. Ovarian cancer spreads very quickly too.
Who are at risk?
- Woman of never having given birth
- Woman who attain first menstrual bleeds before the age of 12
- Woman who attain menopause after the age of 55
- Increase in age
- Woman who have family member with ovarian cancer
- Unexplained loss of weight (losing weight when you are not trying to)
- Woman who had breast cancer
How is Ovarian Cancer Diagnosed?
Sadly, most ovarian cancers are diagnosed in the later stages when survival rates are lower, as mentioned.
This is because the symptoms (as listed above) as you may have noticed are common with many other ailments too and often not severe until later stages – which can't be helped. Who immediately assumes that bloating or nausea has anything to do with ovarian cancer? And to make things more difficult, there are no reliable tests for early detection.
But, if you are high-risk (i.e. have had breast cancer and a family history), your doctor can perform a pelvic exam, a blood test, and an ultrasound.
Your doctor will likely recommend further testing if abnormalities are found. This could include more lab tests, CT scans, PET scans, and a colonoscopy (to rule out bowel issues), among others.
What Treatment Options Are Available for Ovarian Cancer?
The treatment options for ovarian cancer depend on the type of tumour, stage of the cancer, and the age of the patient - among others.
Typically though, the treatment starts out with minor laparoscopic surgery to determine the stage of cancer. After that, doctors may recommend surgery to remove the tumour as well as other organs such as the ovaries and uterus to reduce the chances of it spreading.
Your doctor is also likely to suggest chemotherapy and radiation to kill the remaining cancer cells. It also keeps them from multiplying, especially in patients where the disease is more advanced.
At Caring Gynae, our highly experienced gynaecologists offer compassionate treatment and diagnosis of gynaecological conditions for women through every stage of their life.
